Imagine you are riding in a self-driving car when suddenly, a person comes in front of the car. But instead of stopping instantly the car stops after some time, leading to an accident. This may happen if the car has to send the road data to a faraway central server and then wait for a response before taking action, the time elapsed in between these steps can lead to unforeseen circumstances as seen above.
This all can be avoided with the help of Edge Computing. It’s a technology that processes data very fast by processing it near the source rather than sending it to a faraway server, hence increasing speed and saving bandwidth. In today’s blog, we are going to learn about edge computing in detail.
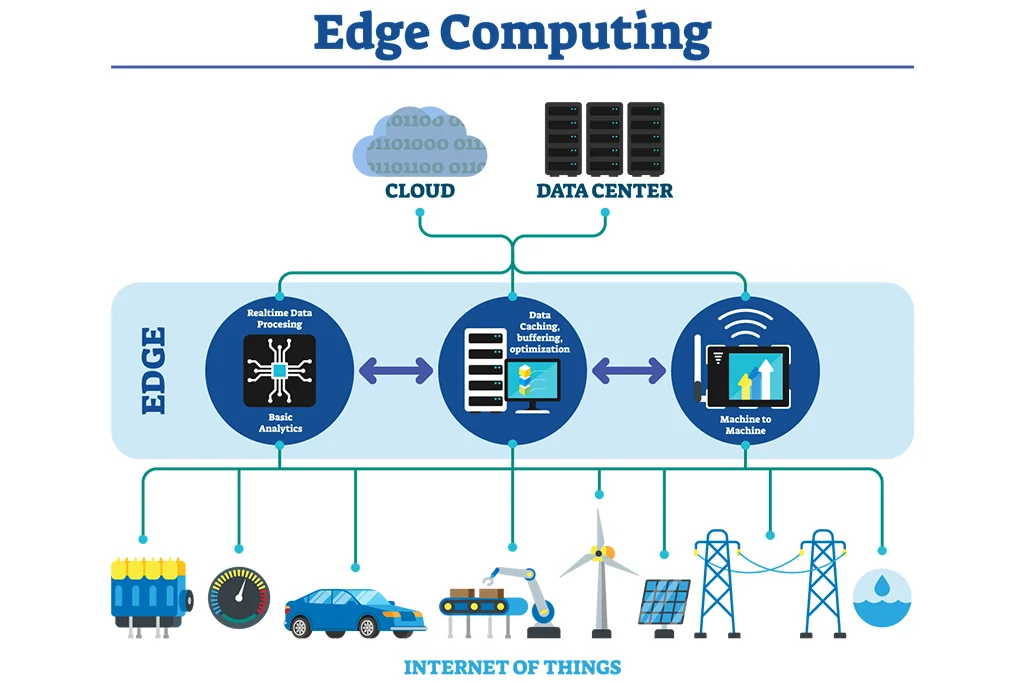
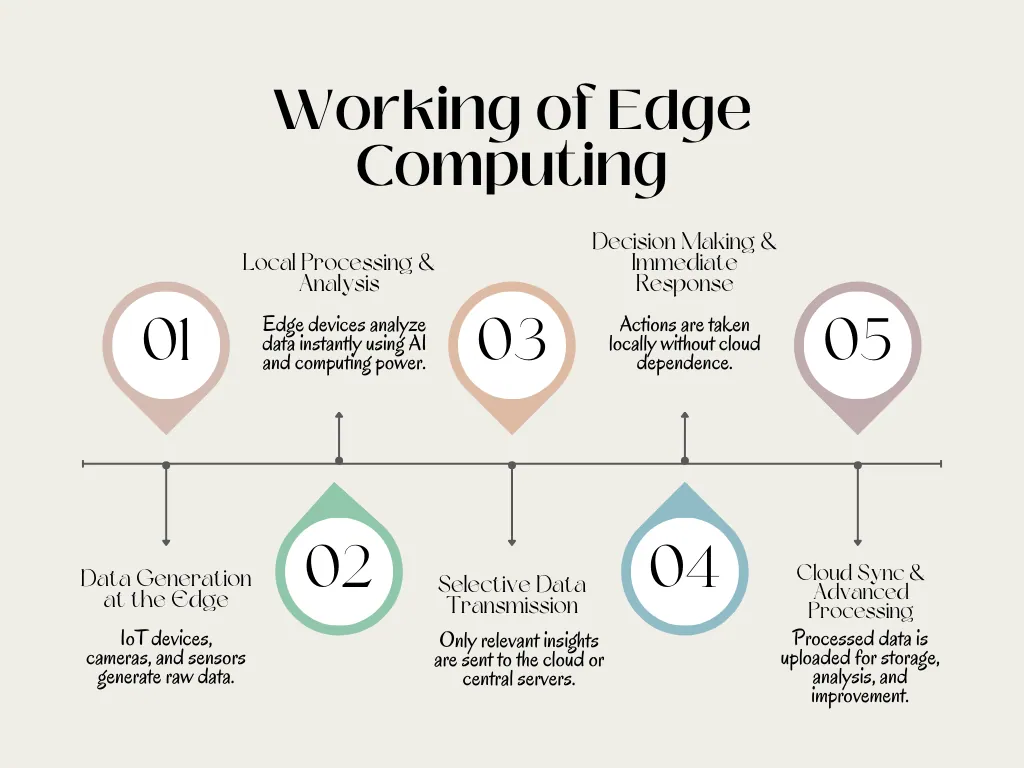
How Does It Work?
Applications of Edge Computing
Now we are going to take a look at some of the most important applications of edge computing and learn how is it transforming various industries.
- It helps autonomous make quick decisions by processing data from sensors and don’t have to wait for information from the cloud.
- It improves real-time rendering, spatial tracking, and immersive experiences by reducing delays in VR/AR applications.
- Edge computing lowers buffering and improves video quality on services like Netflix and YouTube by storing content closer to users.
- It identifies threats instantly at the network’s edge before they impact central systems.
- NASA and other groups use Edge computing to analyze data in space missions where internet connections are weak or not available.
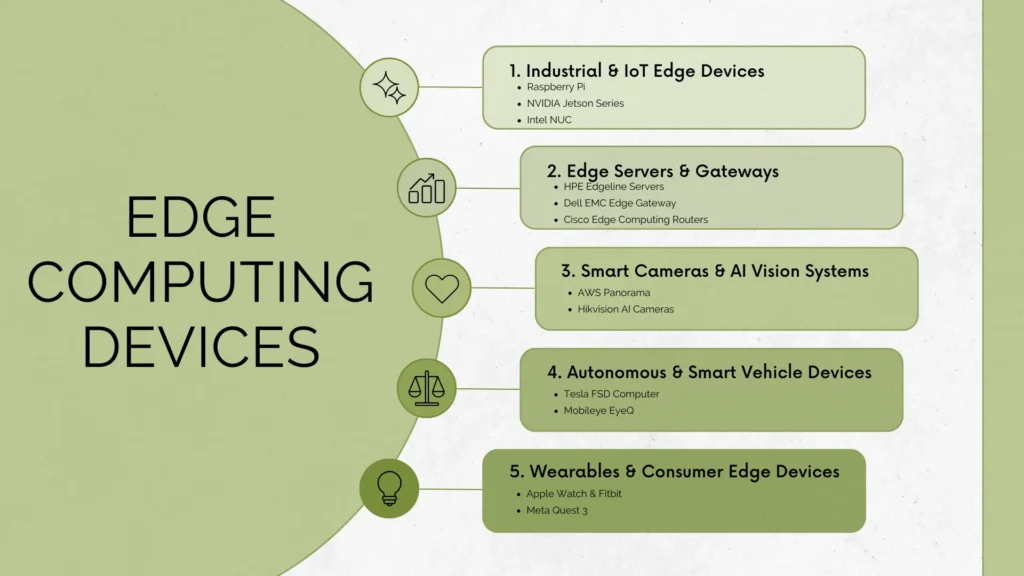
Edge Computing Devices
Comparison
| Features | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Processing Location | Data is processed closer to users like local servers. | Data is processed in centralized data centres located remotely |
| Reliability | It can work offline or with limited connectivity | It requires a stable internet connection. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Has reduced bandwidth usage as data is processed locally. | Has high bandwidth usage due to constant data transfer. |
| Cost Efficiency | Costly for small-scale implementation. | Cost-effective for large-scale storage & computing needs. |
| Power Consumption | Devices may consume more power due to local processing. | Cloud servers do the computing work, which makes it run for a long time. |
| Security and Privacy | It is more secure as sensitive data remains in local servers. | It has an increased chance of data leaks and compliance issues. |
Edge Computing and Cloud Computing both have different use cases, we suggest to use Edge Computing when you need real-time responses and using Cloud Computing for scalable, centralized processing.
Challenges & Limitations
- As data is processed locally or on decentralized networks, there are increased chances of cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
- It is limited to smaller regions, unlike cloud computing. Moreover, it requires additional hardware for expansion.
- Edge devices have less processing power and storage than big cloud data centers.
- There are no common rules or frameworks, thus it has to connect with different IoT and cloud platforms which is sometimes challenging.
- It includes continuous processing which can lead to higher power usage in edge devices, making energy efficiency a concern.
Final Words
We hope that after reading our blog you have gotten an in-depth understanding of Edge Computing, the principle behind it, its applications, limitations and how is it different from cloud computing. As the technology evolves its application will increase and it will transform various industries. What are your thoughts on the future of edge computing? Do let us know in the comments!!! And follow our blogs for more interesting and innovative content.



